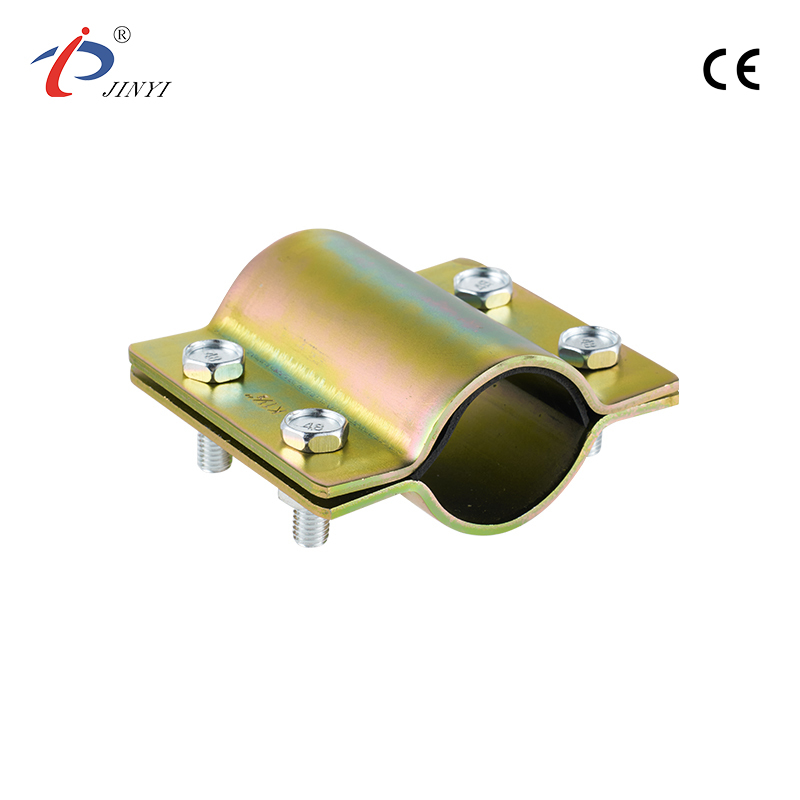
How Do Industrial Clamping Solutions Enhance Safety and Precision
2025-11-10
What Types of China Clamps Are Essential for Industrial Assembly Lines
Industrial assembly lines rely on precise and reliable equipment to ensure smooth operations. Among the tools that maintain efficiency and consistency, China clamps play a critical role. These devices securely hold components during assembly, reducing errors and enabling workers to perform repetitive tasks safely. Selecting the appropriate type depends on the materials, processes, and production goals of the line.
Common Holding Devices in Assembly Lines
Several workholding devices are widely used in industrial settings. Each serves a specific function, and understanding their applications can improve workflow and reduce downtime:
| Clamp Type | Primary Use | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| C-Clamps | General holding and assembly | Easy to adjust, versatile for different sizes |
| Toggle Clamps | Quick securing of parts | Allows fast placement and release, stable during repetitive actions |
| Spring Clamps | Lightweight and temporary holding | Useful for delicate components or small fixtures |
| Bench Clamps | Stationary workholding | Provides stability for precision tasks and supports heavy components |
| Pipe Clamps | Joining tubular materials | Adjustable length, strong grip for various pipe diameters |
Why Device Selection Matters
The right workholding equipment ensures that components remain fixed during soldering, welding, gluing, or mechanical assembly. Improper holding can result in alignment issues, safety risks, and reduced product quality. Production managers often evaluate workflow, material types, and operator handling to determine which options best meet assembly requirements.
Tips for Effective Use
Inspect equipment regularly for wear or fatigue to maintain reliability.
Use devices suitable for the material type and size.
Incorporate adjustable options to accommodate changing product designs.
Train workers on proper handling to reduce the risk of damage or injury.
Adapting Devices to Modern Assembly Lines
With evolving industrial technologies, workholding solutions have become more ergonomic and compatible with automated systems. Pneumatic and hydraulic mechanisms, for example, provide consistent pressure and can integrate into robotic assembly lines. Choosing devices that adapt to both manual and automated processes adds flexibility and efficiency to production.
Holding tools are fundamental for accuracy and stability in industrial assembly lines. By understanding the various types and their applications, manufacturers can ensure reliable performance, maintain smooth operations, and create safer working environments. Proper selection enhances workflow and reduces errors across different production stages.
How Can China Clamps Improve Precision and Safety in Metalworking Operations
Metalworking operations often involve cutting, drilling, bending, and welding processes that require stable and accurate positioning of materials. Using secure holding tools is essential to enhance both precision and safety by keeping components firmly in place during these tasks. By reducing movement and vibrations, these devices contribute to consistent results and help prevent accidents.
Key Roles of Holding Tools in Metalworking
- Maintaining Alignment
- Proper holding ensures that metal sheets, rods, or assemblies stay aligned during fabrication. Misalignment can lead to uneven cuts, imprecise holes, or weak joints. Using the right device minimizes errors and allows operators to achieve uniform outputs consistently.
- Reducing Operator Fatigue
- Holding heavy or awkward metal pieces manually can be tiring and unsafe. Secure fixtures provide steady support, freeing workers to focus on the tool or machine operation rather than constantly adjusting materials. This also reduces the risk of slips or sudden movements.
- Enhancing Safety Measures
- Stable workholding creates a safer workspace by preventing workpieces from shifting unexpectedly. This is especially critical during high-speed cutting or welding, where sudden movement can cause injuries or damage to equipment.
Types of Devices Commonly Used in Metalworking
| Clamp Type | Typical Use | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| C-Clamps | General holding for small to medium parts | Simple and versatile for various projects |
| Toggle Clamps | Securing pieces during repetitive cuts | Fast engagement and release improve workflow |
| Bar Clamps | Holding long or flat metal sections | Provides even pressure across extended surfaces |
| Pipe Clamps | Joining cylindrical materials | Adjustable length accommodates different diameters |
| Magnetic Clamps | Metal positioning for welding | Stable grip without mechanical pressure |
Best Practices for Using Workholding Tools
- Inspect all devices before each use to ensure stability.
- Select fixtures suited to material type, weight, and operation.
- Avoid over-tightening to prevent distortion or surface damage.
- Combine with protective padding when handling delicate metals.
Integration with Automated Metalworking Systems
Modern fabrication facilities often integrate holding tools with automated machinery such as CNC machines or robotic welding stations. Pneumatic or hydraulic devices provide uniform pressure without constant manual intervention, allowing precise operations with consistent safety standards.
Using secure holding tools effectively in metalworking operations improves precision, maintains alignment, and reduces safety risks. Incorporating a variety of devices and following best practices ensures steady workflow, protects operators, and delivers reliable production outcomes.
Which China Clamps Should You Use for Heavy‑Duty Lifting and Rigging Applications
Heavy-duty lifting and rigging operations require reliable equipment to ensure safety and efficiency on worksites. Selecting the appropriate securing devices for cables, beams, and other load-bearing materials is critical. The right tools reduce the risk of accidents, support consistent load control, and allow teams to maintain productivity during complex lifting procedures.
Types of Devices for Rigging and Lifting
There are several categories of holding devices commonly used in industrial lifting:
| Device Type | Primary Use | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Rope Clips | Securing cables and slings | Provides firm grip, reusable and adjustable |
| Beam Clamps | Attaching loads to steel beams | Ensures stable attachment without welding |
| Plate Lifting Clamps | Handling steel plates | Distributes load evenly and reduces slippage |
| Chain Hooks and Shackles | General lifting and securing | Quick connection and flexible for various angles |
Key Considerations for Selection
When choosing devices for lifting or rigging, consider:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with steel, cable, or other materials being lifted.
- Load Capacity: Match the device to the expected weight range and dynamic forces.
- Environmental Conditions: Outdoor operations may require corrosion-resistant options.
- Ease of Use: Devices that allow quick adjustment or positioning enhance workflow efficiency.
Best Practices for Safe Operations
- Inspect all securing equipment before each lift to check for wear, deformation, or fatigue.
- Train operators on proper attachment techniques and alignment to prevent uneven load distribution.
- Avoid overloading devices beyond recommended ranges to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Use secondary safety measures such as safety slings or backup supports for critical lifts.
Integrating Modern Technologies
Recent developments in lifting equipment have introduced ergonomic and mechanically assisted tools. Devices that incorporate adjustable clamping pressure or locking mechanisms improve reliability and reduce manual strain. These innovations are increasingly compatible with cranes, hoists, and automated lifting systems, offering more predictable performance in both small and large-scale operations.
Selecting the right heavy-duty lifting and rigging devices ensures stability, precision, and safety on worksites. By understanding different types and their proper applications, teams can improve operational efficiency, reduce risks, and maintain consistent performance across various lifting tasks. Proper inspection and training further enhance workplace safety and productivity.



 русский
русский  Español
Español